Taurus KEPD 350
| Taurus KEPD-350 | |
|---|---|
 A Taurus on display at the 2006 ILA air show | |
| Type | Air-launched cruise missile, Land-attack missile, Anti-ship missile |
| Place of origin | Germany and Sweden |
| Service history | |
| In service | Since 2006 |
| Used by | Germany, South Korea, Spain |
| Production history | |
| Designer | Taurus Systems GmbH |
| Designed | 1995–2005 |
| Manufacturer | Taurus Systems GmbH |
| Produced | Since 2005 |
| Variants |
|
| Specifications (KEPD 350) | |
| Mass | 1,400 kg (3,100 lb) |
| Length | 5.1 m (16 ft 9 in) |
| Width | 1,080 mm (3 ft 7 in) |
| Height | 805 mm (2 ft 7.7 in) |
| Wingspan | 2.06 m (6 ft 9 in) |
| Warhead | Two‐stage tandem MEPHISTO penetrator |
| Warhead weight | 480 kg (1,060 lb) |
| Engine | Williams P8300‐15 turbofan 680.4 kgf (6,672 N; 1,500 lbf) thrust |
Operational range | > 500 km (270 nmi; 310 mi) |
| Maximum speed | Mach .95 (323 m/s; 1,060 ft/s) |
Guidance system | INS, GPS, image-based navigation (IBN), RADALT |
Steering system | Four tailfins |
Launch platform | Panavia PA-200 Tornado IDS, Saab JAS-39C Gripen, McDonnell Douglas F-15K Slam Eagle, McDonnell Douglas F/A-18A+ Hornet, Eurofighter Typhoon EF-2000 |
| References | Janes[1] |
The Taurus KEPD-350[a] is a German-Swedish air-launched cruise missile, manufactured by Taurus Systems and used by Germany, Spain, and South Korea.[2] Taurus Systems GmbH is a partnership between MBDA Deutschland GmbH (formerly LFK) and Saab Bofors Dynamics.[3]
History
[edit]During the Cold War Germany wanted to buy French Apache missiles, which did not work out. In 1998, Germany funded the development of a powered system to be designated KEPD-350 with the acronym TAURUS (Target Adaptive Unitary and dispensor Robotic Ubiquity System).[4]
Taurus leak
[edit]In February 2024, there was a discussion among Luftwaffe officers as to how the system could be delivered to Ukraine to target the Crimean Bridge. Four officers prepared a briefing for Chancellor Olaf Scholz on the topic at an online meeting. The conversation was conducted via webex.[5] A Russian intelligence service, media suspect the GRU, is reported to have intercepted the conversation and published it on the state controlled channel RT-Deutsch. An English translation of the transcript of the conversation was later posted online, though like various news reports it contains a number of errors.[6]
The leak was followed by a public debate about countering Russian espionage in Germany. MAD started investigations. [7][8]
Overview
[edit]The missile incorporates stealth technology and has an official range in excess of 500 km (300 mi).[9] It is powered by a turbofan engine. It can operate at Mach 0.95 and can be carried by Panavia PA-200 Tornado IDS, Eurofighter Typhoon EF-2000, Saab JAS-39C Gripen, McDonnell Douglas EF-18A+ Hornet, and McDonnell Douglas F-15K Slam Eagle aircraft.[citation needed]
The dual stage 480-kilogram (1,100 lb) warhead, called MEPHISTO (multi-effect penetrator highly sophisticated and target optimised),[10] features a precharge and initial penetrating charge to clear soil or enter "hard and deeply buried targets" (HDBT) such as hardened underground bunkers, then a variable delay fuze to control detonation of the main warhead. The missile weighs about 1,400 kg (3,100 lb) and has a maximum body diameter of 1 metre (3.3 ft). Intended targets are hardened bunkers; command, control, and communications facilities; airfield and port facilities; ammunition storage facilities; ships in port or at sea; area target attack; and bridges.[11]
Operation
[edit]Mission planners program the missile with the target, air defence locations and planned ground path. The missile uses a terrain-hugging flight path, guided by inertial navigation system (INS), image based navigation (IBN), terrain referenced navigation (TRN), and Global Positioning System (GPS) to the target. It is capable of navigating over long distances without GPS support.[12][13]
Upon arrival the missile commences a bunt (climb) manoeuvre to achieve the best probability of target acquisition and penetration. During the cruise portion of the flight, a high resolution thermographic camera (infrared homing) can support navigation by using IBN and for GPS-free target attack. The missile attempts to match a camera image with the planned 3D target model (Digital Scene Matching Area Correlator, DSMAC). If it cannot, it defaults to the other navigation systems, or, to avoid collateral damage, it steers to a pre-designated crash point instead of risking an inaccurate attack.[citation needed]
Export
[edit]Spain's military bought 45 missiles. Integration of the missile in Spanish Air Force service was certified by completing a dedicated test campaign in South Africa in May 2009.[14]
In 2013 South Korea planned to order 200 missiles to integrate with their F-15K Slam Eagles after it was prevented from acquiring Lockheed Martin's AGM-158 JASSM by the United States.[15] The Defense Acquisition Program Administration (DAPA) signed the deal in November 2013. The KEPD 350 was the first European missile to be integrated onto a South Korean fighter.[16] In October 2016, South Korea announced it would acquire a further 90 missiles, in addition to the 170 previously ordered, in response to North Korean nuclear and missile provocations.[17] On 12 December 2016, the first 40 Taurus KEPD 350K missiles were delivered to the ROKAF.[18][19]
In May 2023, the German Federal Ministry of Defence said that Ukraine had requested the missile during the ongoing Russian invasion of Ukraine.[20] In interviews in June and July 2023, German Chancellor Olaf Scholz and Minister of Defense Boris Pistorius said that Germany would not supply Ukraine with long-range missiles.[21][22][23] In January 2024, the German Bundestag voted against the supply of the Taurus missile to Ukraine.[24] In February 2024, the German Bundestag and Chancellor Olaf Scholz again expressly refused Ukraine's request while agreeing to deliver longer range weapons.[25][26]
Variants
[edit]
KEPD 350K
[edit]The variant for the ROKAF differs from the baseline model by being equipped with a Rockwell Collins GPS receiver with a Selective Availability Anti-Spoofing Module (SAASM) to prevent jamming.[27]
KEPD 350K-2
[edit]In October 2015, Taurus Systems revealed it was developing a smaller version of the Taurus missile, called the 350K-2, for use on light fighters, particularly the South Korean FA-50 Block 20 variant of the KAI T-50 Golden Eagle.[28] It is shorter at 4.5 m (15 ft) in length and lighter, weighing 907 kg (2,000 lb) while matching speed and range.[29]
In December 2016, South Korea's Defense Acquisition Program Administration (DAPA) announced plans to start development on a long-range air-to-ground missile in 2018, based on Taurus. The weapon was to be mounted on the KAI KF-21 Boramae fighter, to be developed by the mid-2020s.[30]
Taurus Neo
[edit]On 27 October 2024, Boris Pistorius (German Defence Minister) announced a next generation Taurus missile called the Taurus Neo. With plans to purchase 600 units costing some €2.1 billion with deliveries starting in 2029. The Taurus Neo will include a range over 500 kms, a more powerful warhead and better guidance. 300 million euros would be required in 2025 to start the program.[31][32]
Operators
[edit]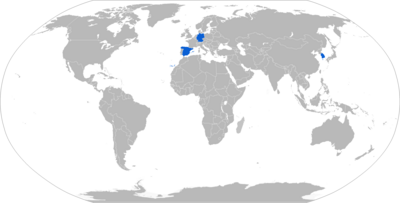
Current operators
[edit] Germany
Germany- 600 ordered for the Luftwaffe's Panavia PA-200 Tornado IDS and Eurofighter Typhoon EF-2000 at a cost of €570 million.[33] Deliveries ended in December 2010.[34][35]
 Spain
Spain- 43 ordered for the Spanish Air Force's McDonnell Douglas EF-18A+ Hornets and Eurofighter Typhoon EF-2000.[36] Deliveries ended in August 2010.[35] The program cost €60m.[37]
 South Korea
South Korea- 177 ordered in 2013, delivered in 2016–2017, 90 ordered in 2018, delivered in 2019–2020, and to be operated from the Republic of Korea Air Force's McDonnell Douglas F-15K Slam Eagle fighter jets.[38][39]
See also
[edit]- AGM-158 JASSM – American low observable air-launched cruise missile
- HOPE/HOSBO – German, family of precision-guided glide bombs
- KD-88 – Chinese anti-ship cruise missile
- Ra'ad (air-launched cruise missile)
- Ra'ad-II – Air-launched cruise missile
- SOM (missile) – Turkish air-launched cruise missile
- Storm Shadow – Franco-British cruise missile
- YJ-22 – Chinese cruise missile
- CJ-10 – Chinese cruise missile
- Brahmos – Supersonic Cruise missile, jointly developed by India and Russia
- Wan Chien – Taiwanese air-launched cruise missile
- Joint Strike Missile – Norwegian/American air-launched cruise missile
- Fateh Mobin – Iranian short-range ballistic missile
Notes
[edit]- ^ Target Adaptive Unitary and Dispenser Robotic Ubiquity System/Kinetic Energy Penetrator and Destroyer.[citation needed]
References
[edit]- ^ Janes (21 November 2023), "Taurus KEPD 350", Janes Weapons: Air Launched, Coulsdon, Surrey: Jane's Group UK Limited., retrieved 6 February 2024
- ^ "Abstandslenkflugkörpersystem: Erste Taurus an Südkorea übergeben". Archived from the original on 13 September 2017. Retrieved 23 October 2016.
- ^ "Gripen Multi-Role Fighter Aircraft, Sweden". Airforce technology. Projects. Retrieved 17 July 2007.
- ^ "EADS/Bofors TAURUS". 23 June 2011. Archived from the original on 23 June 2011. Retrieved 18 January 2024.
- ^ deutschlandfunk.de. "Spionageverdacht bei der Bundeswehr - Was bisher über den Fall bekannt ist". Die Nachrichten (in German). Retrieved 4 March 2024.
- ^ "Full Transcript of German Top Military Officials' Leaked Plot to Attack Crimean Bridge", Bundle, March 2024. Available at: https://www.bundle.app/en/breakingNews/full-transcript-of-german-top-military-officials'-leaked-plot-to-attack-crimean-bridge-15a59c62-f695-4d07-852d-788455d17230
- ^ "Bundeswehr abgehört: Union stellt Scholz' Glaubwürdigkeit infrage". tagesschau.de (in German). Retrieved 4 March 2024.
- ^ "Luftwaffe-Leaks: "Ein Informationskrieg, den Putin führt" – Augen geradeaus!". augengeradeaus.net. Retrieved 4 March 2024.
- ^ "Kepd 350". DE: Taurus systems. Archived from the original on 27 September 2007. Retrieved 3 September 2007.
- ^ "First Taurus Cruise Missiles for Korea". C4Defence. 14 October 2016. Archived from the original on 15 July 2017. Retrieved 13 September 2017.
- ^ TAURUS final (Motion picture). TAURUS systems GmbH. Archived from the original on 29 July 2020.
- ^ "Kepd 350". Defence Update. Archived from the original on March 2, 2012. Retrieved May 6, 2008.
- ^ Taurus KEPD 350 the modular stand-off missile for precision strike (PDF), MBDA Deutschland GmbH, archived from the original (PDF) on 15 November 2012
- ^ "El Ejército del Aire incrementa su capacidad operativa con la integración del misil Taurus en el F-18". Ejercito del aire (in Spanish). ES: MDE. Archived from the original on December 23, 2009. Retrieved June 15, 2009.
- ^ "S. Korea to buy bunker busting missiles from Europe". Reuters. 4 April 2013. Retrieved 7 April 2013.
- ^ "Taurus Systems to open Seoul office this week", The Korea Times, 11 May 2014.
- ^ "South Korea plans to buy more Taurus missiles after North Korea's new nuclear test". www.airrecognition.com. Retrieved 26 February 2024.
- ^ "First batch of 40 Taurus KEPD 350K cruise missiles arrived in South Korea". airrecognition.com. Retrieved 26 February 2024.
- ^ "South Korea starts deploying Taurus cruise missile for combat use". airrecognition.com. Retrieved 26 February 2024.
- ^ Ukraine asks Germany to provide Taurus long-range missiles - Berlin - Reuters.com, 27 May 2023
- ^ Germany denies Ukraine's plea for Taurus missiles to help counter Russian air power - AlArabiya.net, 2 July, 2023
- ^ Gazeta.ua (27 June 2023). "Німеччина відмовляється надати ЗСУ далекобійні ракети Taurus". Gazeta.ua (in Ukrainian). Retrieved 26 February 2024.
- ^ "Через две недели ФРГ примет решение по истребителям Украине – DW – 05.06.2023". dw.com (in Russian). Retrieved 26 February 2024.
- ^ Hasselbach, Christoph. "Ukraine: Germany will not supply Taurus cruise missiles". Deutsche Welle. Retrieved 24 January 2024.
- ^ "Germany's Scholz rules out sending long-range Taurus missiles to Ukraine". www.aa.com.tr. Retrieved 26 February 2024.
- ^ "Germany's Bundestag votes against Taurus missiles to Ukraine". Deutsche Welle. Retrieved 22 February 2024.
- ^ Jennings, Gareth (14 October 2016). "South Korea begins receiving Taurus cruise missiles". Jane's Information Group. Retrieved 13 December 2016.
- ^ "South Korea plans to arm its FA-50 light combat fighters with new variant of the Taurus missile". www.airrecognition.com. Retrieved 26 February 2024.
- ^ "Taurus-LIG Nex1 developing KEPD 350K-2 for FA-50". Janes Information Services. 8 December 2023. Archived from the original on 20 December 2023.
- ^ "South Korea plans to develop Taurus-based air-to-ground missile". airrecognition.com. Retrieved 26 February 2024.
- ^ "Germany to Develop Next-Gen Taurus Neo Cruise Missile after Ukraine War Lessons". armyrecognition. 29 October 2024. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- ^ Sabine Siebold (25 October 2024). "German defence minister seeks to develop advanced Taurus missiles, source says". Reuters. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- ^ "Taurus". EADS. Archived from the original on 29 June 2012. Retrieved 11 September 2007.
- ^ "MBDA Delivers 600th TAURUS KEPD 350 to German Luftwaffe" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 23 March 2020.
- ^ a b Hoyle, Craig (14 December 2010). "Germany receives last Taurus cruise missile". Flight Global. Retrieved 26 February 2024.
- ^ Principales programas (in Spanish), Spain: MDE, archived from the original on 20 October 2008.
- ^ "Evaluación de los Programas Especiales de Armamento (PEAs), Ministerio de Defensa" (PDF). Atenea (in Spanish). Madrid: Grupo Atenea. September 2011. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 October 2013. Retrieved 30 September 2012.
- ^ "(LEAD) S. Korea buys more Taurus missiles amid N.K. nuke threats". South Korea: Yonhap. 4 October 2016. Retrieved 4 October 2016.
- ^ Mizokami, Kyle (10 July 2017). "This Is How South Korea Plans to Stop a Nuclear Attack from North Korea". The National Interest. Retrieved 5 January 2019.
External links
[edit]- Taurus Systems GmbH, DE.
- TAURUSKEPD 350 – HigH precision STAnD-off (PDF), SAAB AB Dynamic, archived (PDF) from the original on 28 May 2015
- "TAURUS KEPD 350E". Archived from the original on 22 November 2019.
